Prepared by:
Ibtihal Iftikhar (G14)
Muhammad Abdul Rehman Wazir (G14)
Compiled by:
Hafiz Muhammad Umair Noor (G12)
Reference Books:
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry 8th Edition
- Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry 30th Edition
- Satyanarayana Biochemistry 6th Edition
- Essential of Medical Biochemistry by Mushtaq Ahmed 9th edition
Cell: (F-B-001, F-B-002, F-B-004)
- Same as cell physiology, if you have prepared that well just revise it
- In addition read chapter 1 from Satya and especially the difference table in that chapter between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
- Do the following diseases: I cell disease, Parkinsonism, Progeria, Refsum disease from Satya and the table given here.


Signal Transduction: (F-B-003)
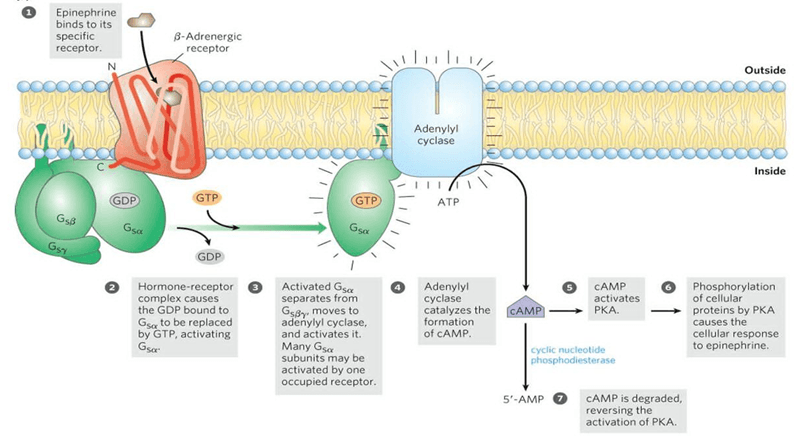
- Do fig 8.7 8.8 & 17.8 (practice drawing them as they’re very imp)
- cAMP system pg 103, 104, 105, fig 8.5, 8.7, 8.8
- Phospholipase C system pg 228, fig 17.8
- The side box of vibrio cholera and whooping cough
- Def of signal transduction and importance/uses of G-protein coupled receptor, pictures are given below:




Tidbits:
- Signal Transduction: process by which physical or chemical signals are transmitted through cell as a series of molecular events, particularly phosphorylation by protein kinases.
- Intracellular signals
- Extracellular signals
- Juxtacrine Signaling: signaling that requires close contact, a ligand on one surface attaches to receptor on the other.
- By secreting molecules:
- Endocrine (in blood)
- Paracrine (to nearby cells)
- Synaptic (through synapses)
- Autocrine (to cells own self)
DNA & RNA: (F-B-006, F-B-007)
Most imp topics from Satya chapter 5 are given below:
- Chargaff’s Rule and DNA double helix, and learn to draw the schematic diagram of DNA
- Different forms of DNA (A, B & Z)
- Names of other types of DNA structures (Bent, triple stranded etc.)
- Organization of DNA along with diagram
- Definition of melting temp and renaturation
- Focus on everything under topic of RNA
- Pay special attention to learning to draw structure of transfer RNA
Nucleotides: (F-B-005, F-B-008)
- Start with first 3 topics only of Chapter Nucleic Acids in Mushtaq (Ch 14)
- Do biomedical importance of natural and synthetic analogues from Satya chapter 5 (Purine, Pyrimidine and Nucleotide Analogs topic) as well as look at minor bases found in nucleic acids
Chromosome: (F-B-009)
- Do higher organization of DNA from Lippincott chapter 30 page 473, 474 (eukaryotic DNA organization)
- Also refer to the diagram below
- Difference:
- DNA: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for an organism.
- Chromatin: DNA is packaged with proteins (like histones) to form a complex called chromatin.
- Chromosome: A chromosome is a structure made up of DNA and proteins, where DNA is tightly coiled and packaged.
- Chromatid: Before cell division, a chromosome replicates, resulting in two identical copies called sister chromatids. These sister chromatids are joined at a region called the centromere.
- Cell Division: During cell division (mitosis or meiosis), the sister chromatids separate, and each becomes an individual chromosome in the daughter cells.
- Analogy: Think of a chromosome as a “house” and the chromatids as the two identical “floors” of that house.

Enzymes: (F-B-010)
Best channel for concept of enzymes is Medicosis Perfectionalis on Youtube
- Do enzymes with reference to active site, specificity etc. from Lippincott chapter 5
- Do nomenclature from Lippincott chapter 5
- Do classification of enzymes from Lippincott fig 5.1 (keep in mind a new 7th class of enzymes Translocases)
- Do Mechanism of action, Factors, Michaelis Menten Kinetics, Lineweaver Burk plot and Competitive and Non-competitive inhibition from Lippincott chapter 5
- Fig 5.12 and 5.14 are vvvvvv imp
- Do Uncompetitive Inhibition of enzymes from Mushtaq chapter 6 and Medicosis Perfectionalis
- Leave the topic of Enzyme Regulation as it is not mentioned in the syllabus
- Do therapeutic use of enzymes from Satya table 6.8
- For enzymes used in clinical diagnostics Do Lippincott table 5.2, also do the heading of isozymes on page 70
- Do table 6.1 and 6.6 to 6.13 from Satya
- For zymogens read passage in Mushtaq under topic properties of enzymes in chapter 6
Amino acids: (F-B-011)
- Do classification of amino acids based on polarity from Lippincott fig 1.2 and 1.3
- Do structural n dietary classification from Satya chapter 4 page 46 to 51 (skip polarity based classification from Satya as it is wrong)
- Do metabolic classification of proteins from Lippincott fig 20.2.
- Do structure (page 46), physical and chemical properties (page 51, 52, 53) of amino acids from Satya chapter 4
- Do biomedical importance of amino acids from Satya chapter 4 page 55
- Do functions of individual amino acids from the pic shared in group (pic reference Lippincott chapter 20 page 305 summary)
Note: If there’s any conflict between the classifications on Lippincott and Satya, prefer Lippincott
Protein: (F-B-012)
- Do classification of proteins from Satya chapter 4 page 67, 68.
- Do biomedical importance of proteins from Satya chapter 4 page 68, 69 (biologically imp peptides)
- For class A and B proteins pictures are shared in the group
- Do Structural levels of proteins from Lippincott chap 2
- You should be very clear about the difference in alpha helix and beta pleated sheets, the types of stabilizing interactions between proteins at each level, examples of each structural level.
- Do the Role Of Chaperones from pg 21 Lippincott.
- Do biochemical basis of disorders of proteins misfolding from Lippincott chapter 2
- You should be very clear about the biochemical basis of diseases, e.g.
Biochemical basis of Alzheimer’s: It is a deposition of amyloid beta plaques in brain parenchyma. (The simpler, the better)
Plasma Proteins: (F-B-013)
- Do plasma proteins from Satya chapter 9
- Remember the class of plasma proteins e.g. transferrin is a beta globulin
Immunoglobulins: (F-B-014)
- Do structure and biomedical importance of immunoglobulins from Satya chapter 9
- Do functions of immunoglobulins from Satya chapter 9
- Production, structure and function of plasma cells, b cells is covered in Guyton chp 35. Do it from there.
- Do interleukins from Guyton chp 35 pg 467 “ Specific regulatory functions of lymphokines’’ and table 35.1.
- Platelet Activating Factor (PAF) from Guyton pg 478 first paragraph.
- PDGF from Guyton pg 477 first paragraph point no. 6
- Do multiple myeloma from Satya chapter 9 page 189, 19
- Labs for interpretation of multiple myeloma:
- M spike in electrophoretic pattern of serum proteins (Also keep in mind the normal electrophoretic pattern)
- Bence Jones proteins in urine
- Raised plasma immunoglobulin levels
Pro Tip: You can make your own notes for plasma proteins and immunoglobulins by combining all the relevant information from biochem and physio while preparing for block. These notes will be your go to resource for quick rev during proff and it will save a lot of your time. However, it is not advisable to get yourself busy making notes during the proff days.