Prepared by:
Hassan e Muhammad (G14)
Compiled by:
Hafiz Muhammad Umair Noor (G12)
Recommended Book:
- Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 14th Edition (Chapter numbers are mentioned according to this edition)
Reference Books:
- Jaypee Essentials of Medical Physiology 6th Edition
MEMBRANE PHYSIOLOGY
Chapter 5:
MS-P-001:
- Membrane potentials across selectively permeable membrane pg 63 (read for Basic concept + mcqs)
MS-P-002:
- Normal distribution of Ca Cl Na and K across membrane from fig 4.1
- Membrane potential vs Nerst potential
- Nernst potential and it’s basis
- Nernst equation (calculate the nernst potential for Na and K by putting values in the equation)
MS-P-003:
- Goldman Equation pg 64 imp(use to calculate diffusion potential & resting potential when membrane is permeable to several different ions)
MS-P-004:
- Resting membrane potential of neurons pg 65
- Table 5.1 (mcqs)
- Fig 5.5
- Origin of RMP (seq) & physiological basis i.e factors contributing
- Hyperkalemia and Hypokalemia( imp) ( pic is shared in the group)
- Membrane Stabilizers ( lidocaine, calcium, mexiletine, valproic acid)
- Inhibition of excitability stabilizers and local anesthetics pg 76 ( v imp) and their mechanism of action
MS-P-007:
- Neuron action potential pg 67 (definition+ all stages)
- Fig 5.6 imp ( also do it from the pic shared in the group )
- Voltage gated Na and K channels
- Na channels can be blocked by tetrodotoxin when applied outside the cell membrane (mcq)
- K channels can be blocked by tetraethylammonium ion when applied to interior of nerve fibre (mcq)
- Initiation of action potential pg 71( read)
- Propagation of action potential (read)
- All or nothing principle pg 72 (imp)
- Re establishing Na and K ionic gradients after action potential pg 72 (imp)
- Properties of action potential (pic is shared in the group)
- Monophasic action potential (pic is shared in the group)
- Refractory period ( pic is shared in the group) relative v/s absolute
MS-P-008:
- Role of Other ions during action potential pg 70 blue box ( v imp + tetany is seq ) role of Ca+ in it
- Rheobase , chronaxie , utilization time ( vimp pic is shared in the group)
MS-P-011:
- Special characteristics of signal transmission in nerve trunks (imp) pg 74
- saltatory conduction and its importance
Chapter 31: (Jaypee)
MS-P-009(a):
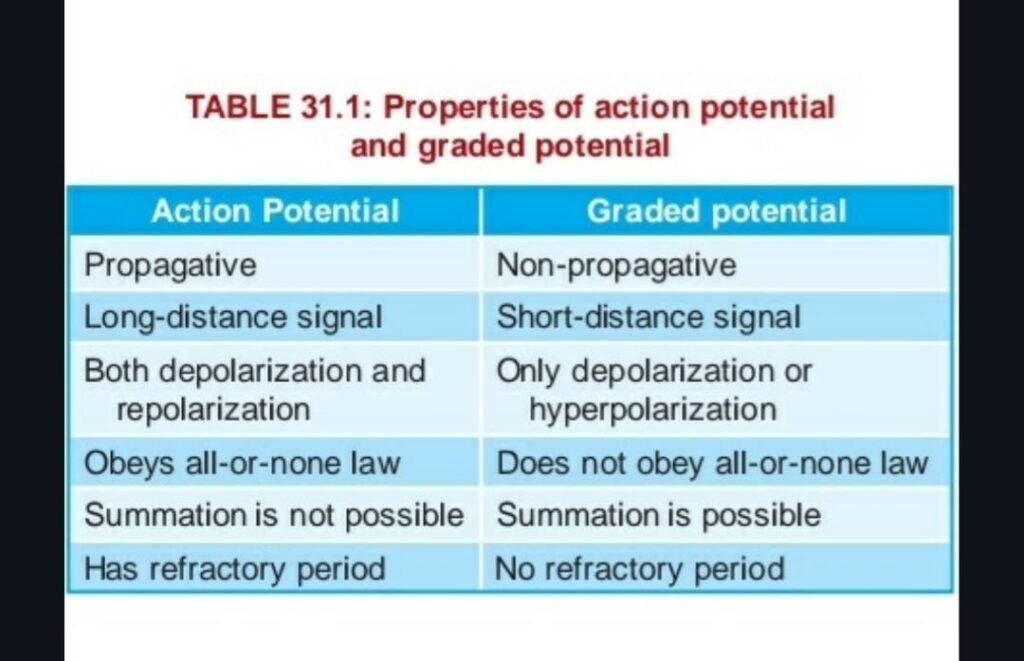
- Graded potential + table 31.1 basis& properties
- Graded vs Action Potential difference
- Compound Action Potential .. basis& properties

NERVE PHYSIOLOGY
Chapter 134:(Jaypee)
MS-P-005(a):
- Complete chapter till functionsof neurilemma
- Neuron anatomy
- Neuron classification
- Myelin sheath, neurilemma
Chapter 138: (Jaypee)
MS-P-005(b):
- Complete chapter
- Neuroglial cells and their roles
- Myelination process
- Axonal transport ( pic is shared in the group)
Chapter 135: (Jaypee)
MS-P-006:
- Complete chapter
- Nerve fibers classification table 135.1
Chapter 140: (Jaypee)
MS-P-009(b): Synapse
- Fig 140.4
- Fig 140.5
MS-P-010:
- Functional classification of synapse
- Fig 140.2 +140.3
Chapter 137: (Jaypee)
MS-P-012:
- Multiple Sclerosis
- GB syndrome (google)
- Causes, features and pathophysiology
- Degeneration of neuron two types
- Regeneration of neuron
MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
Chapter 6:
MS-P-013:
- Physiological anatomy of skeltal muscle
- Sarcomere
- Fig 6.3
- Jaypee Table 28.1 (Diference)
MS-P-014:
- Charcteristics of muscle contraction
- Fig 6.12
- Also do examples Of Isotonic and isometric contraction
- Fast vs slow muscle fibres
MS-P-015:
- Motor unit
- Force summation
- Multiple summation
- Frequency summation and tetanization (imp)
- Treppe
- muscle fatigue
- Remodeling +Blue box
Chapter 7:
MS-P-016:
- Complete Chapter
- Anatomy, generation and conduction of impulse at NMJ
- Generation of endplate potential
- Excitation and contractions coupling (imp)
- Myasthenia Gravis (v.imp )
- NMJ enhancer and inhibitors
Chapter 8:
MS-P-017:
- Types of Smooth Muscle
- Physiologivcal basis Of Smooth Muscle contraction
- Smooth muscle contraction without Action Potential
- Hormones causing contractions without Action Potential
- Latch mechanism and importance
- Stress Relaxation
- Regulation By Calcium
- Nervous and hormonal Control (Complete till end)

