Prepared by:
Kisa e Zahra (G12)
Compiled by:
Hafiz Muhammad Umair Noor (G12)
Reference Books:
- Anwar Microbiology 2nd Edition
- Sketchy Microbiology
Note:
- Sketchy + Anwar (this is the best combo for micro and you have to prepared everything in this)
- You can also use Levinson as it is standard book for your better understanding.
(ID-Pa-001)
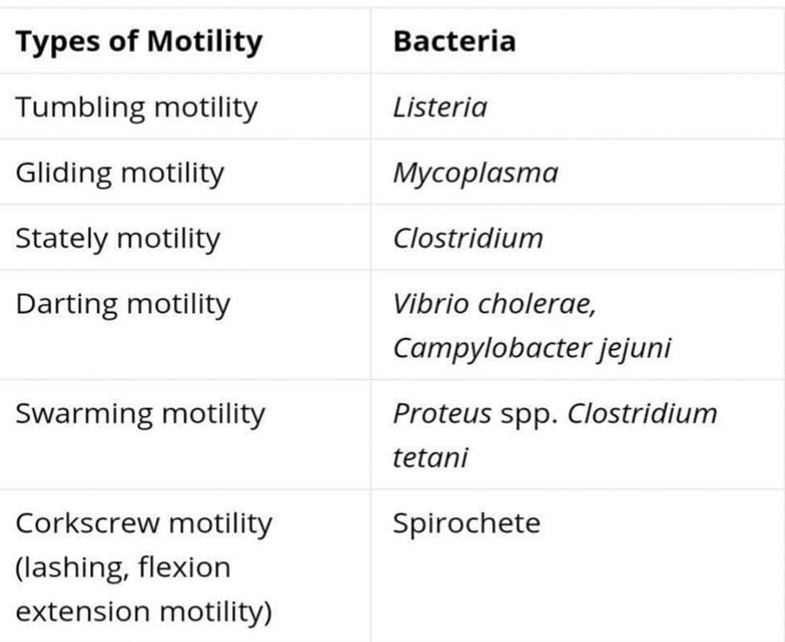
For clinical bacteriology basic steps are always on your fingertips like staining, morphology, virulence factors, special disease by microbe etc
Gram +ve Microbes
Anwar Chapter # 12, 14
Levinson Chapter # 15, 17 (All tables are imp)
IMPORTANT POINTS FOR BACTERIA
- Staph aureus ( all diseases caused by this(Kawasaki disease and other), its cell wall components and pathogenisis
- For strep know about it’s hemolysis classification and strep pyogenese is imp one
- Clostridium classification+imp diseases caused by them
- Bacillus (imp) caused by reheated rice
- Corynebacterium pathogenisis and diseases imp
- Read of listeria and gardenella
Gram -ve Cocci
Anwar Chapter # 13
Levinson Chapter # 16
- Neisseria species are imp (specially their pathogenesis and lab diagnosis)
Gram -ve Rods:
Lab diagnosis are important that will differ microbes like MacCkoney’s agar, urease test, TSI test colour.
Anwar Chapter #15
Levinson Chapter # 18+19
- E.coli (most imp) it’s pathogenesis, it’s ETEC and EHEC form and lab diagnosis
- Salmonella (imp pathogenesis, rose spots, lab diagnosis)
- Shigella (pathogenesis)
- Vibrio (imp pathogenesis+ rice watery stools + lab diagnosis)
- Proteus (pathogenesis+ urease positive + staghorn canaliculi)
- Pseudomonas (imp pigments + diseases + patho)
- H.pylori and camplylobacter (read+ sketchy)
- Actinomyces (only sketchy)
Spirochetes:
Anwar Chapter # 21
Levinson Chapter # 24
- Traponema (imp one it’s types, patho, lab diagnosis)
- Borrelia and leptospira (read)
Mycobacterium:
Anwar Chapter # 18
Levinson Chapter # 21
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis is most imp . Should done everything ( pathogenesis, diseases, lab diagnosis imp)
- Laprae( imp and it’s two types difference)
Rickettsia and Chlymadia:
Anwar Chapter # 22, 23
- Just do sketchy and anwar

(D-Pa-002)
- For parasites most imp are life cycles and the most of transmission
- Sketchy and Anwar are best for context and do life cycles from Levinson
Anwar Chapter # 44, 45, 46, 47, 48
Levinson Chapter # 51, 52, 54, 55, 56
IMPORTANT PARASITES
- Entamoeba
- Plasmodium (very imp)
- Echinococcus(life cycle imp)
- Shictosoma
- Entrobius
- Ascaris
- Necator
- Ancylostoma
(Note: do each and everything of above mention parasites)
(ID-Pa-003)
For fungi (Anwar + sketchy is enough)
Anwar Chapter # 40, 41, 42
IMPORTANT FUNGI
- Dermatophytes (type+ lab diagnosis)
- Histoplasma imp (morphology+ pathogenesis)
- Candida (most imp) (patho+ clinical findings+ lab diagnosis)
- Cryptococcus (patho+ lab diagnosis)
- Aspergillus (imp patho+ it’s forms + lab diagnosis)
(ID-Pa-004)
- Virology is tough from others microbes just do imp viruses
- Sketchy and Anwar is more than enough
- Always remember imp points that will help in diagnosis
Anwar Chapter # 31
- Herpes+ varicella + cytomegalovirus are imp one
- Others just read
Anwar Chapter # 32
- Influenza (important it’s types+ antigenic drift and shift and pathogenisis factors
- Measles mumps (sketchy is enough and read from Anwar)
- Rabies most imp) (it’s pathogenesis and incubation period and vaccine)
- Rubella (read)
Anwar Chapter # 33
- Corona virus (important it’s pathogenesis)
Anwar Chapter # 34
- Polio virus (imp) (it’s mode of transmission + pathogenesis + it’s vaccine types)
- Reovirus (read)
Anwar Chapter # 35
- Hepatitis B is most imp among them
- Serological findings
- Clinical features
- Pathogenesis
- Window period
- Read other hepatitis types
Anwar Chapter # 36
- Dengue virus (very imp)
- Dengue hemorrhagic fever hypothesis
- Lab diagnosis
Anwar Chapter # 37
- Just do table
Anwar Chapter # 38
- HIV (most imp)
- Pathogenesis
- Cycle
- Stages of AIDS
- Lab diagnosis
(Note: Do sktechy must for microbiology)
(ID-Pa-005)
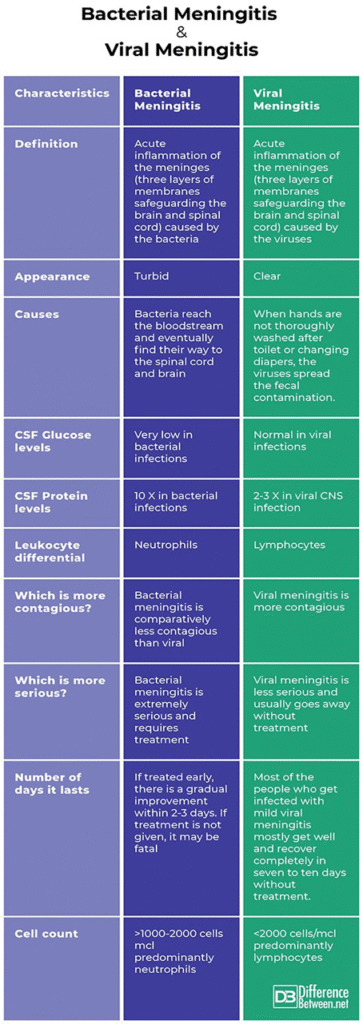
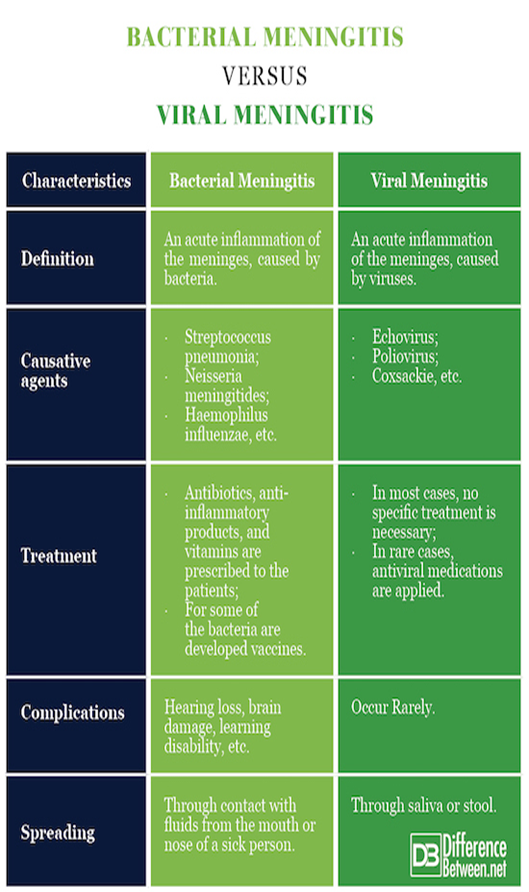
Microbes Causing CNS Infections
For meningitis this will help:
- Less than 2 Months (Neonates and Young Infants)
- Streptococcus Agalactiae (Group B Streptococcus
- Escherichia Coli (E. coli)
- Listeria Monocytogenes
- More than 2 Months (Infants and Young Children)
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Pneumococcus)
- Neisseria Meningitidis (Meningococcus)
- Important Note: If a child is unvaccinated then Haemophilus influenzae becomes a very significant, often the number 1 cause of bacterial meningitis in this age group.
- 2-18 Years (Children and Adolescents)
- Neisseria Meningitidis (Meningococcus)
- More than 18 Years (Adults)
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Pneumococcus
- Immunocompromised Individuals (e.g. HIV positive, Drug Users)
- Listeria Monocytogenes
(Note: Correlate above knowledge)
(ID-Pa-006)
- GIT problems
- Correlate above knowledge
- Hepatitis guidelines mention in virology part
- Entamoeba in parasitic part
(ID-Pa-007)
- GIT infections
- Correlate from above knowledge
(ID-Pa-008)
- Rickettsia and leptospira mention in above bacteriology guidelines
- Anthrax, plague,francisella, bartonella and Brucella (do table from Anwar chapter17 and sketchy)

