Prepared by:
Alisha Athar (G13)
Usman Qaisar (G13)
Compiled by:
Talha Saleem (G12)
Recommended Book:
- Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 14th Edition (Chapter numbers are mentioned according to this edition)
SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
NS-P-001,002
Chapter 46:
- Start from pg 572, Central nervous system synapses.
- Types of synapses (imp + learn difference from google )
- Physiologic anatomy of synapses (read)
- Transmitter release from presynaptic terminals (role of Ca) (read)
- Transmitter actions on postsynaptic neurons (functions of receptor proteins)
- Just shortlist Ion channels paragraph
- Excitation and inhibition at post synaptic membrane
- Table 46.1(imp)
- Table 46.2
- Difference b/w small and large (neuropeptides) molecule transmitter (pic attached)
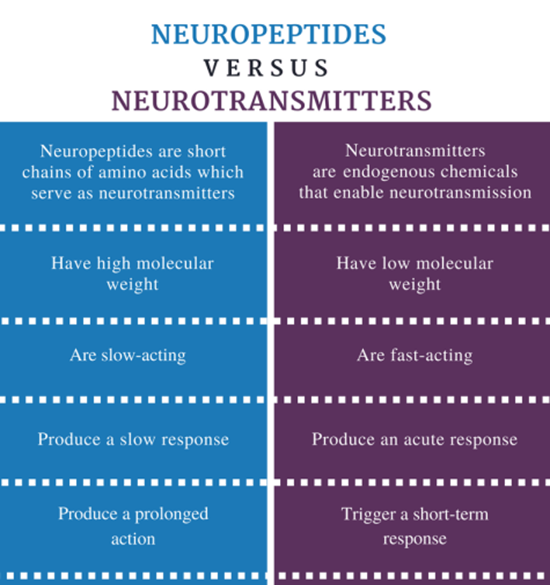
- Characteristics of some imp small molecule transmitters (location , excitatory / inhibitory) pg 578
- Spatial summation and temporal summation (imp)
- Special characteristics of synaptic transmission (imp)
Chapter 47:
- Types of sensory receptors
- Table 47.1
- Differential sensitivity ( read)
- Labeled line principle (SEQ) (imp)
- Properties of receptors (from Jaypee chapter 139)
- Receptor potentials (complete) (SEQ)
- Adaptation of receptors with mechanisms (UQ) (imp)
- Types of adaptation + examples (v imp)
- Read fig 47.5
- Classification of nerve fibres ( blue box) + (jaypee chapter 135)
- Fig 47.6
- Divergence signal from neuronal pool with types and examples (imp) proff mcqs
- Convergence of signals with types n examples (imp) proff mcqs
NS-P-003
- These los will be covered from snell neuroanatomy chapter 8
- Personal neglect syndrome (google)
NS-P-004,005,006
Chapter 48:
- Classification of somatic senses with other classification
- Types of all receptors, location, speed, capsule, adaptation and sensations (imp)
- Transmission of tactile signals
- Detection of vibration
- Detection of tickle
- Sensory pathways (most imp)
- Blue box (v imp)pg 601
- DCML with fig 48.3 (v imp) ( make your own detailed diagram from snell neuroanatomy)
- Spatial orientation of nerve fibres in DCML
- Somatosensory cortex
- Somatosensory areas I and II difference
- Fig 48.6 (seq)
- Fig 48.7 (seq)
- Spatial orientation of signals from different parts of body in somatosensory Area 1
- Functions of somatosensory area I (imp)
- Somatosensory association areas (SEQ) (v imp)
- Amorphothesis (imp)
- Characteristics of DCML signal transmission and analysis ( read for understanding scenario)
- Anterolateral pathway(imp) with fig 48.13( make your own detailed diagram from snell neuroanatomy)
- Difference b/w DCML and Anterolateral pathway ( google)
- Blue box (function of thalamus in somatic sensation + corticofugal signals )
NS-P-007
Chapter 49:
- Fast pain and slow pain qualities + other names
- Fast Pain and slow Pain ( difference) vvimp
- Pain receptors and their stimulation with all subheadings ( read)
- Dual pain pathway (neo spinothalamic and Paleo spinothalamic)(complete topic with fig 49.2 , fig 49.3)
- Pain suppression (analgesia) (imp)
- Fig 49.4
- Brain opiate system
- Inhibition of pain transmission by tactile receptors (blue box)
- Referred pain with fig 49.5(imp)(UQ)
- Causes of visceral pain ( read)
- Parietal pain (read)
- Brown sequard syndrome (vvimp) written in blue box
MOTOR PHYSIOLOGY
Note:
- It’s quite complex, so it’s better to study it from both Snell Neuroanatomy and Guyton, if you combine both, it will be easy to understand, first you should do neuro then physio because some concepts are related to neuroanatomy and others to physiology.
- General functions from Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology
- Pathways and circuits from Snell Neuroanatomy
Chapter 55
- Organization of spinal cord (last para)
- Anterior motor neurons (alpha and gamma) (imp)
- Interneurons (imp)
- Renshaw cells (imp)
- Muscle sensory receptors (imp)
- Receptor functions of muscle spindle (SEQ)
- Primary ending and secondary ending
- Types of fibers in muscle spindle
- Static response and dynamic response (imp)
- Muscle stretch reflex (UQ) with fig 55.5
- Damping definition
- Voluntary motor control of muscle spindle
- Brain areas for gamma motor control
- Stabilize body position
- Summarize all functions of muscle spindle (imp)
- Golgi tendon reflex (UQ)
- Fig 55.8
- Lengthening reaction (imp)
- Flexor reflex, fig 55.9
- Crossed extensor reflex (imp)
- Spinal shock with features (imp)
- Give a read to reflex arc, its components and types from Firdous physiology
Chapter 56:
- Motor cortex, it’s sub area
- Fig 56.1 (UQ)
- Primary motor cortex with functions
- Premotor cortex it’s function
- Supplementary motor cortex it’s functions
- Specialized areas of motor control, all with location and removal effects
- Corticospinal tract ( fig56.4)
- Rubrospinal tract is accessory pathway for transmission of discrete signals (read)
- Effect of lesion in motor cortex
- Role of brain stem (6 points)
- Decerebrate animal spastic rigidity (imp)
- Vestibular sensations and maintaince of equilibrium (compl)
Chapter 57:
- Cerebellum and it’s functions (imp)
- Anatomical and functional areas of cerebellum
- Fig 57.2 (imp)
- Functions of cerebellum (vestibuli cerebellum, spinocerebellum, cerebri cerebellum) (imp)
- Clinical abnormality of cerebellum (UQ)(Complete)
- Basal ganglia and it’s functions
- Putamen circuit (imp)
- Fig 57.11 (imp)
- Abnormal function of Putamen circuit, athetosis (imp), chorea, hemiballismus (imp)
- Change timing amd scale intensity
- Role of basal ganglia in cognitive control, the caudate circuit (imp)
- Function of specific neurotransmitters (fig 57.14)
- Parkinson’s disease (UQ), it’s each cause, mechanism and treatment
- Huntington disease (imp)
Chapter 58:
- Association areas, location of each area (fig 58.5)
- Higher intellectual functions till working memory
- Thoughts consciousness and memory till end
Chapter 59:
- Limbic system it’s functions
- Functional anatomy +Fig 59.5
- Hypothalamus fig 59.6
- Effects caused by hypothalamic lesions
- Reward centre and punishment centre
- Specific functions
- Functions of amygdala
- Kluver bucy syndrome(Imp)
Chapter 60: (Important)
- Sleep def and types of sleep
- Difference b/w REM and NREM
- Neural centers of sleep
- Lesion of sleep center
- Other neurotransmitters
- Possible cause
- Brain waves (UQ), each wave (arise from, voltage, cycles)
- Changes in EEG
- Epilepsy (UQ)
- Types of epilepsy (imp)
- Alzheimer’s disease (imp)
Chapter 61:
- Difference b/w sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves
- General organization including box
- Basic characteristics
- Table 61.1
- Table 61.2
- Alarm and stress response of sympathetic nervous system

