Prepared by:
Chaman Zulfiqar (G12)
Compiled by:
Hafiz Muhammad Umair Noor (G12)
Reference Books:
- NRA Forensic Medicine 2nd Edition
- Shahbaz Forensic Medicine 6th Edition
For2-Tr-001:
- Chapter 5, def of injury, wound, hurt with their section number
- Def must be learnt word to word as it is
- Page 109 Injuries classification on basis of causative agent complete topic
- Table 4.2 NRA complete as it is vvv imp
For2-Tr-002:
- Chapter 5 SHAHBAZ, pg 107, mech of wound production complete
For2-Tr-003:
- Chapter 5 SHAHBAZ , pg 113 to 114 complete topic of abrasion
For2-Tr-004:
- Chapter 5 SHAHBAZ pg 110 to 112, bruise, complete topic along with tables + table 6.3 from NRA vvv imp table
For2-Tr-005:
- Chapter 5 SHAHBAZ, pg 115 to 116 Laceration complete topic + table of diff b/w laceration, incised wound and stab wound on SHAHBAZ pg 123 sendup question
For2-Tr-006:
- Not given in book, you’ll have to do it from google or chat/gpt
For2-Tr-007:
- SHAHBAZ chap 5 pg 116 to 121, incised and stab wounds complete
For2-Tr-008:
- Mainly related to pathology
For2-Tr-009:
- SHAHBAZ chap 5, pg 125 age of wound, complete topic till next page
For2-Tr-010:
- Ewings postulate, from NRA (given at end of traumatology chap)
For2-Tr-011:
- Chapter 15 SHAHBAZ, pg 322 battered baby syndrome, comp topic
For2-Tr-012 For2-Tr-013
- These topics will be covered in your lab and wards
For2-Tr-014:
- Chap 6 SHAHBAZ, def of firearm pg, 127
- Firearm components + def of ballistics, pg 129
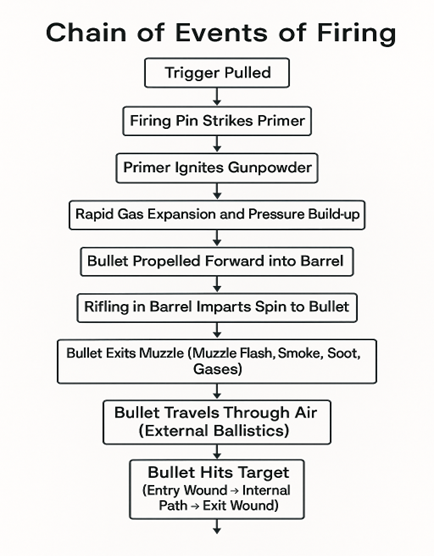
For2-Tr-015:
- Chapter 6 SHAHBAZ, pg 133, exterior ballistics ke last pr 2 points h air resistance aur gravity wale ye topic krna ha
For2-Tr-016:
- Chapter 6 SHAHBAZ, firearm wound complex + pg 145 determination of dist of fire + pg 142, table of diff b/w entry and exit wound
For2-Tr-017:
- Chapter 6 SHAHBAZ, pg 132 gun powder types and composition
For2-Tr-018:
- Complete topic of explosions from SHAHBAZ, pg 33, not much imp
For2-Tr-019 and For2-Tr-020
- complete topic of pedestriam injuries from SHAHBAZ pg 326 to 322
For2-Tr-021:
- Chapter 7 SHAHBAZ Thermal injury complete topic till pg 162
For2-Tr-022:
- Chapter 7 SHAHBAZ, pg 164 till end complete topic of electrocution and lightening
For2-Tr-023:
- SHAHBAZ pg 348, complete topic of heat (mcqs ae the hme is topic se test me, so don’t ignore it)
For2-Tr-024:
- Covered in topic of burns
For2-Tr-025:
- SHAHBAZ Chapter 8, pg 188, complete topic of drowning
For2-Se-001:
- SHAHBAZ Chapter 9 pg 195, all def + causes of impotence from next pg along with medicolegal imp from pg 197
For2-Se-002:
- SHAHBAZ Chapter 10, signs of viriginity, complete topic + medicolegal imp from pg 207
For2-Se-003:
- Chapter 10 SHAHBAZ, signs of pregnancy, complete topic, pg 207
For2-Se-004:
- Chapter 10, Signs of delivery, complete topic
For2-Se-005:
- Chapter 10 SHAHBAZ, pg 217 abortion complete topic (criminal abortion is extremely imp)
For2-Se-006:
- SHAHBAZ Chapter 11, def of sexual offences, classificatio, legal consideration, examination of case of rape (it’s written very lengthy here, do it from NRA) extremely imp topic (ques of our prof exam)
For2-Se-007:
- SHAHBAZ Chapter 15, Def of infanticide + summary of factors indicative of live birth from pg 318,
- Definition of live born, still born, dead born, and table differentiating b/w ante-natal and intra-natal deaths, from pg 312
- Their autopsy findings are not mentioned here properly. You can do it from google