Prepared by:
Hanzala Masood (G14)
Compiled by:
Zuha Iftikhar (G14)
Recommended Book:
- BD Chaurasia Human Anatomy 8th Edition
- Snell’s Clinical Anatomy by Regions 10th Edition
Muscles:
- All muscles from tables of Snell with nerve supply and action (Especially remember actions of muscles as they are v imp)
- Muscles of hypothenar eminence(College block 2 SEQ)
- Also thoroughly go through muscles on model or 3D app because in PROFF we were asked to locate a particular muscle on muscle model and tell it’s action.
Nerves:
- All nerves are very important (Root value ,Course, Muscles supplied by nerve ,branches, lesions covered in clinicals)
- From Appendix of BD
- (Sometimes they are not covered from appendix. If, then study each nerve separately in respective chapters of BD and try to combine the course and branches in the form of your own notes) Otherwise go for Snell.
- From Appendix of BD
- Preferable to do all nerves from Snell as clinicals are mostly asked from Snell
- Musculocutaneous Nerve
- Axillary nerve (College block 2 SEQ)
- Radial nerve
- Median nerve
- Ulnar nerve
Clinicals:
From pdf shared
- Must give a good read to clinicals from Snell as lines of Snell were given in mcqs in PROFF 2024
No need to do surface landmarks and only some fasciae are important
For Gross Anatomy:
- Try to visualize things first from Atlas/ Atlas app
- and then read book. In this subject , thing can only be remembered when you properly visualize it and then read the book. Also, Revision is the key for retention of content.
Lecture sources that can be used:
- Dr.Azam , Johari Mbbs , Essentials of medical science , TCML others
- Practice MCQs are v.imp in Gross especially scenarios.
- Use BRS Gross Anatomy for practicing scenario MCQs (highly recommended) as well as past papers.
Chapter 2:
- Bones (Snell’s Anatomy Diagram + Bone models)
- In PROFF 2024 No diagram of Snell was given Bone was given on which different landmarks like tubercles/trochanters/ etc. were asked.
- Follow following points for any bone:
- Carefully listen to lecture
- Watch video lecture of bone ( Johari MBBS, Angelina Issac ,others) those which elaborate bone on 3D model or original bone model
- Take the bone model and then study diff. aspects like features/attachments/landmarks on that model.
- Do bones from BD and only bone diagram from Snell for OSPE purpose.
- Try to make a voice note/recorded note of Bones and nerves and listen to it often to revise and your topic will be revised in max 5-7 min( it’s a beneficial way. You can go for this method if it suits you)
(This method would be helpful in both theory and OSPE In sha Allah)
- Things asked from bones in written exam are mainly ATTACHMENTS & CLINICALS.
- Side determination
- Features
- Attachments Just do superficially for imp muscles. Also do important ligaments like suprascapular/glenoidal labra etc.
- All clinicals
- skip ossification
- Just do the names and arrangement of carpel bones (skip everything else related to it also skip metacarpals and phalanges)
Chapter 3:
- Superficial fascia (give a good read to its contents i.e. cutaneous vessels and nerves for mcqs)
- Platysma ( muscle of facial expression) v.imp (complete)
- Breast v.v.imp(do complete topic except development and histology)
- lymph drainage of breast v.v.imp ( you can watch Johari mbbs lecture for this)
- Also do clinicals( amastia polymastia polythelia etc)
- Clavipectoral fascia and structures passing through it (complete topic) v imp
Chapter 4: IMP
- Axilla v.v.imp
- introduction
- base + walls (v.imp)
- contents imp
- Axillary artery complete with relations of it’s all three parts
- v.v.v.imp (make mnemonics for relations)
- Branches of Axillary artery v.imp complete
- Axillary vein (course + tributaries + drainage)
- Axillary lymph nodes imp ( you can watch Essentials of medical science video for this topic)
- Diagram of Axillary Inlet vv.imp (PROFF 2023 SEQ) from Snell
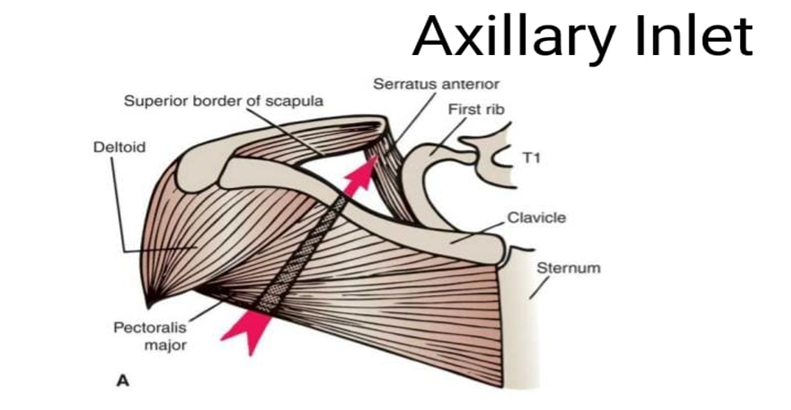
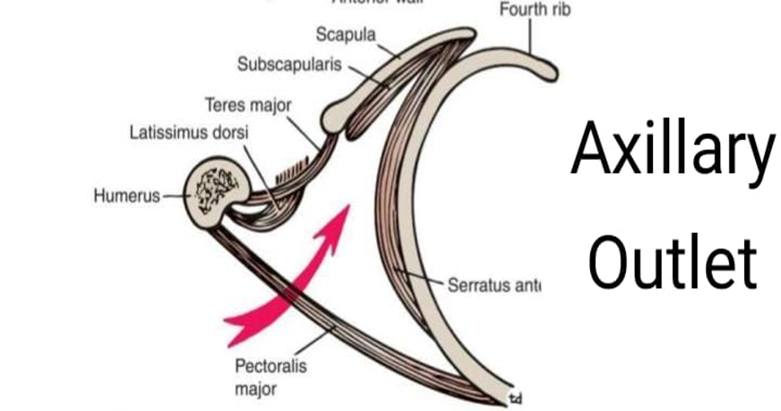
- Axillary artery is ligated commonly between its 1st part and subscapular artery in case of its blockage or trauma (PROFF 2024 SEQ)
- Brachial plexus vvv.imp most imp topic of this chapter:
- Many Qs are asked from entire topic and especially it’s clinicals
- do complete topic (skip sympathetic innervation)
- its diagram v.v.imp (learn to draw it with all it’s cords and branches)
- Its clinicals will be covered in
- Clinicals pdf + Snell
- Erb’s Duchenne + Klumpke’s paralysis v.v.imp
- For Brachial plexus you can take NINJA NERD lecture (thoroughly covered)
Chapter 5:
- Triangle of auscultation v imp (PROFF 2024 SEQ SUPP)
- Lumber triangle of petit
Chapter 6:
- Three parts of deltoid muscle with their actions
- Rotator cuff v.imp
- Subacromial bursa v.imp
- Intermuscular space v.imp ( you can take TCML lecture) imp.
- Anastomosis around scapula (vvv.imp) also know how to draw it as it’s diagram is (PROFF 2024 SEQ)
Chapter 7:
- Cutaneous innervation diagram + dermatome diagram do it from netter atlas
- also, you should know how to draw cutaneous innervation and dermatomes (Selfless medicose videos or MBS medi lectures videos)
- Table 7.1 imp complete (leave root values)
- Dermatome def only
- Superficial vein imp (at least give a very good read to all three veins )
- Lymphatic drainage of Upper limb (watch any video and try to do it in a flowchart) – almost similar to lymph drainage of axilla
Chapter 8:
- Compartments of arm (give a good read)
- Anastomosis around elbow v.v.imp
- complete topic
- also learn how to draw it as it is asked in exams
- Cubital fossa, everything is vv.imp (don’t do the details of content)
- Profunda brachii artery imp (complete course + branches)
- Brachial Artery (course+ branches) branches v.imp only name
Chapter 9:
- Synovial Sheaths of Flexor Tendons (not that much imp) give it a good read for concept
- Vincula longa + brevis imp
- Palmar aspect of wrist and hand imp
- Flexor retinaculum (vvv imp) complete topic
- Palmar Aponeurosis (vv imp) complete
- Fibrous Flexor Sheaths of the Fingers (clinically)
- Fascial spaces of hand v.imp (complete topic + table 9.7)
- Synovial sheaths (digital synovial sheaths +ulnar radial bursa)
- Anatomical snuffbox v.v.imp (complete topic)
- Extensor retinaculum (complete attachments + compartments- table 9.8) v imp
- Arches of hand (read for concept)
- Doral digital expansion (extensor expansion) read
- Arteries:
- Radial artery( course and branches in forearm and hand )
- Ulnar artery( course and branches in forearm and hand
- Superficial and deep palmar arches of hand
Note: Try to extract the book content and make your own notes for arteries and arches
Chapter 10:
- First Cover all BONES and MUSCLES along with their actions. After bones and muscles, all joints will become quite easy
- You’ve to do Type, Variety, Articular Surfaces, Ligaments, Blood Supply, Innervation of joints
- Joints movements & muscles involved in each movement v.v.imp
- Sternoclavicular + Acromioclavicular joint for viva & MCQ only ( do remember the type and other main things)
- Shoulder joint v.v.v.imp
- Type
- Articular surfaces
- Stability factors
- Ligaments v.imp
- Skip relations
- Bursas blood and nerve supply
- Movements (only 4 points) + muscles involved (table 10.1 from BD)
- Skip overhead movement
- Read scapulohumeral mechanism from SNELL (In our college block ospe we were asked to demonstrate this on humerus and scapula and angles were asked & also in proff, joint model was given and name type and other Qs were asked)
- Elbow joint (vvv imp seq) complete, except Relations -Carrying angle from SNELL.
- Radioulnar joint just read the table 10.2 for viva & MCQ, leave the rest
- Wrist joint complete seq imp except relation also do it’s ligaments from SNELL.
- 1st carpometacarpal joint (seq vvv imp) complete BD
- Do only the type of rest of the joints for mcq/viva ( must do types of all joints)
- Preferable to do WRIST JOINT and ELBOW JOINT from Snell
- if you have time then go through ligaments of joints and Types of joints from snell
- From ligaments you have to do names only but if you have time then also try to remember it’s point of attachment on participating bones
Anatomy seems difficult but once you start doing it the right way, it will become your favorite.
All the best!